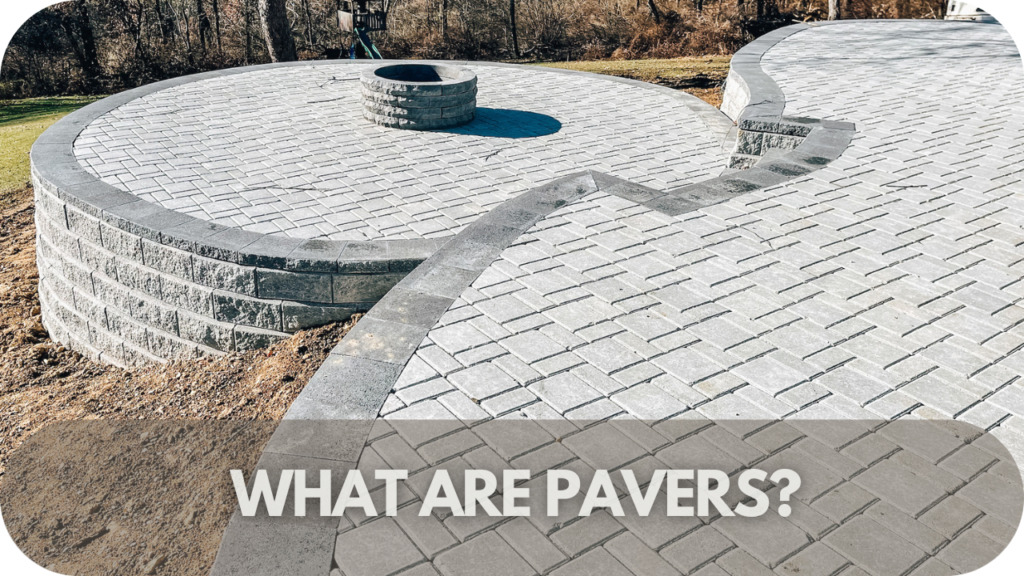
The Best Marble Pavers for Classy Outdoor Spaces
Tired of bland outdoor spaces lacking sophistication?
Imagine stepping into your backyard and feeling underwhelmed by the uninspiring concrete or generic pavers underfoot. It’s a missed opportunity for elegance and style, leaving your outdoor oasis feeling lacklustre and ordinary.
Enter the solution: exquisite marble pavers. Elevate your outdoor space with timeless beauty, unmatched durability, and luxurious appeal. Explore the top picks for infusing your outdoor haven with class and charm.
Top Marble Pavers for Outdoor Spaces
Elevating your outdoor space with marble pavers offers abundant choices. Explore the top contenders, each offering distinct features and benefits for various outdoor settings.
1. Luna Grey Marble Pavers
- Unique Features: These pavers boast a distinctive grey hue with natural veining, adding character and depth to any outdoor area.
- Best Uses: Ideal for patios, walkways, and pool decks, Luna Grey Marble Pavers exude elegance in high-traffic zones.
- Benefits: Beyond their elegant appearance, they’re exceptionally durable, standing the test of time against the elements.
2. El Capitan Marble Pavers
- Unique Features: Warm, earthy tones and a textured finish lend these pavers a rustic charm, perfect for creating inviting outdoor spaces.
- Best Uses: El Capitan Marble Pavers are well-suited for driveways, garden paths, and outdoor seating areas due to their robustness and slip resistance.
- Benefits: They offer durability, and their textured surface ensures safety, especially in moisture-prone areas.
3. Verde Marble Pavers
- Unique Features: The rich green colour and natural patterns imbue these pavers with a distinctive aesthetic, evoking a sense of natural beauty.
- Best Uses: Perfect for garden walkways and decorative accents, Verde Marble Pavers seamlessly blend with lush outdoor environments.
- Benefits: Beyond their visual appeal, they add a touch of nature to outdoor spaces, creating a serene atmosphere.
4. Atmos Marble Pavers
- Unique Features: Soft, neutral tones and a smooth finish give Atmos Marble Pavers a sophisticated allure suitable for various design schemes.
- Best Uses: From courtyards to formal outdoor spaces, these versatile pavers complement a range of architectural styles.
- Benefits: Offering both versatility and a refined look, Atmos Marble Pavers effortlessly enhance the ambience of any outdoor setting.
Design Ideas for Classy Outdoor Spaces
Transforming your outdoor space into a classy oasis with marble pavers is not just about selecting the right stones but also how you incorporate them into your design.
Here are some design ideas to elevate your outdoor areas:
Incorporating Marble Pavers into Patios
- Layout Ideas: Opt for a classic grid pattern for a timeless look, or get creative with herringbone or basket-weave layouts for added visual interest.
- Complementary Materials: Pair marble pavers with natural stone, wood decking, or metal accents to create a sophisticated, balanced aesthetic.
Enhancing Walkways and Pathways
- Creative Designs: Experiment with curved pathways to add flow and intrigue to your outdoor space, or create geometric patterns using contrasting paver colours for a modern twist.
- Border Options: Define walkways with borders made of contrasting pavers, bricks, or even low shrubs for a polished and cohesive look.
Using Marble Pavers Around Pools
- Safety Considerations: Textured marble pavers will provide slip resistance around the pool area, ensuring the safety of your family and guests.
- Aesthetic Benefits: Marble pavers’ reflective surface can enhance the visual appeal of your pool area, creating a luxurious and inviting atmosphere.
Creating Outdoor Living Areas
- Combining with Outdoor Furniture: Pair marble pavers with sleek and modern outdoor furniture for a contemporary look. Opt for rustic pieces to create a cosy and inviting outdoor living space.
- Adding Decor: Incorporate outdoor rugs, throw pillows, and potted plants to add warmth and personality to your outdoor living area, seamlessly blending comfort and style.
Installation Tips for Marble Pavers
Careful preparation and attention to detail are essential for successfully installing marble pavers in your outdoor space. Start by measuring and marking the area to ensure accurate placement of the pavers.
Choose a suitable base material, such as crushed stone or sand, and ensure it is properly compacted and levelled.
When laying the pavers, maintain proper alignment and spacing to create a uniform and visually appealing surface. Consider hiring professionals for complex installations or large areas, as they have the expertise and tools to ensure a flawless finish.
However, DIY installation is feasible for smaller projects with proper research and preparation. Follow step-by-step guides and use the right tools and techniques for a successful outcome.
Whether you opt for professional assistance or tackle the project, attention to detail and precision are crucial for achieving a classy outdoor space with marble pavers.
Maintenance and Care for Marble Pavers
Maintaining the classy allure of your outdoor space adorned with marble pavers requires regular care and attention.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to keeping your marble pavers looking pristine:
Regular Cleaning Practices
Regular cleaning is essential to maintaining the natural beauty of marble pavers. Use a mild detergent and water solution to remove dirt, debris, and stains.
Avoid acidic or abrasive cleaners, as they can damage the surface of the marble.
Consider carefully using a specialised marble cleaner for stubborn stains, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Preventing Stains and Buildup
Prevention is key to keeping marble pavers looking their best. To prevent staining, promptly clean up spills, especially those from acidic substances like wine or citrus juices.
Avoid placing hot objects directly on the surface of the pavers, as this can cause discolouration.
Additionally, regularly sweep or hose down the pavers to prevent the buildup of dirt and debris.
Sealing and Protecting Marble Pavers
Sealing marble pavers helps to protect them from stains, moisture, and wear, prolonging their lifespan and maintaining their appearance.
Choose a high-quality penetrating sealer specifically designed for marble surfaces. Apply the sealer according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring thorough coverage.
To maintain optimal protection, reseal the pavers every 1 to 3 years or as the manufacturer recommends.
Repair and Restoration Tips
Despite your best efforts, marble pavers may experience minor damage over time. Address small chips, scratches, or cracks promptly to prevent further deterioration.
Follow the product instructions carefully when using a marble repair kit or epoxy resin filler to fill damaged areas.
Consult a qualified stone restoration specialist for more extensive damage or professional restoration services.
Conclusion
Marble pavers epitomise timeless elegance for outdoor spaces. With careful selection, installation, and maintenance, they promise enduring beauty and sophistication.
Elevate your outdoor oasis with marble pavers and transform it into a style sanctuary. Take the first step towards creating your dream outdoor space.